5 TEXTILES
- Both natural and synthetic fibres can be woven to make a variety of textiles.
- Natural fibres may come from animal sources (wool, silk), plant sources (cotton, linen, esparto, bamboo) and mineral sources (gold, silver and copper fibres)
- Syntgetic fibres, such as nylon polyester, rayon and Lycra, are plastic materials
sábado, 20 de mayo de 2017
MODIFICATION TECHNIQUES
4 MODIFICATION TECHNIQUES
- Modification techniques use tools and machines to make changes to prefabricated materials, such as sheets, bars or mouldings.
- Examples of thes techniques include: measuring-drawing marks and lines-cutting-drilling-filing and sanding-joining.
- You must always pay special attention to health and safety rules
- Modification techniques use tools and machines to make changes to prefabricated materials, such as sheets, bars or mouldings.
- Examples of thes techniques include: measuring-drawing marks and lines-cutting-drilling-filing and sanding-joining.
- You must always pay special attention to health and safety rules
PLASTIC FORMING TCHNIQUES
3 PLASTIC FORMING TCHNIQUES
- Various industrial teghniques can be used to manufacture plastic products, sush as: extrusion, calendering, vacuum forming and moulding.
- The main techniques for using moulds are as follow: blow moulding, injection moulding and compression mulding
- Various industrial teghniques can be used to manufacture plastic products, sush as: extrusion, calendering, vacuum forming and moulding.
- The main techniques for using moulds are as follow: blow moulding, injection moulding and compression mulding
THE CLASSIFICATION OF PLASTIC
2 THE CLASSIFICATION OF PLASTIC.
- Thermoplastics are usually made from petroleun products. The most common thermospastic are:
- Thermoplastics are usually made from petroleun products. The most common thermospastic are:
- Polyethylene terephthalate
- High-density polyethylene
- Polyvinyl chloride
- Low-density polyethylene
- Polpropylene
- Moulded polystyrene
- Expanded polystyrene or Styrofoam

- Thermosetting plastics are made from petroleum products. They include:
Plastic materials
1.PLASTIC MATERIALS
- Plastics consist of long chains of atoms which are mostly composed of carbon.
- Plastic can be classified into natural and synthetic plastic.
- The process of manufacturing plastic is called polymerisation .
- Plastic materials are resistant, insualting, ductile, malleable, impermeable and light.
- there are three type of plastic recycling processes: chemical and mechanical recycling and energy recovery.
lunes, 15 de mayo de 2017
Electronics
Electronics involves the study of circuit and components that modify the intensity, direction or properties of electric currents.
Electronic components
In this section, we will analyse the most common electronic components.
-Fixed resistance or resistor
A fixed resistance or resistor opposes the flow of electric currents. Its calue, which we measure in ohms, is indicated by code of colour and numbers
Electronic components
In this section, we will analyse the most common electronic components.
-Fixed resistance or resistor
A fixed resistance or resistor opposes the flow of electric currents. Its calue, which we measure in ohms, is indicated by code of colour and numbers
Variable resistance or potentiometer
The value of a variable resistance or potentiometer can be adjusted between zero and the maximum value specifed by the manufacturer
Resistance that depend on a physical factor
Resistance that depends on temperature is called a thermistor. There are two types of thermistors:
-Negative temperature coefficient (NTC): The resistance decreases as the temperature rises.
-Positive temperature coefficient (PTC): The resistance increases as the temperature rise.
LDR: Resistance that varies according to the amoint of light received. the resistance decreases as the amount of light increases. These devices, like potentiometers, are often used in security systemns, where they are parts of sensors
Capacitors
A capacitor can store electrical energy from a battery and then use it to power a light bulb until the charge is totally depleted.
Capacitors are components that can store an elctrical charge.
The value of a capacitor indicates the charge in volts that it can store. This is measured in farads (F)
Diodes
A diode is an electronic component made from semiconductor materials. It only allows electric current to flow in one direction. A diode has two electrodes: an anode (A) and cathode (k)
A LED only gives off light when an electric current flows though it.
martes, 25 de abril de 2017
Electromagnetic control systems
Activates the various parts of a macine, at the right movement and for the right amount of time, ensuring that the machine functions properly.
Cam switch controller
The device on the side of the pulley in the pictures above is called cam. The shape of this device allows us to control the moment and duration of an activity, such as the rinning of a motor or the illumination of a light bulb
Cam switch controller
The device on the side of the pulley in the pictures above is called cam. The shape of this device allows us to control the moment and duration of an activity, such as the rinning of a motor or the illumination of a light bulb
Limit switches
The picture below show an electrical control system for a water tank. THe battery provides power for the pump, which moves water from the lower tank to the upper tank. When the upper tank is full a limit switch turns off the pump.
There are two types of limit switch:
martes, 11 de abril de 2017
ELECTRONAGNETIC MECHANISM
Electromagnetic mechanism are devices that can covert movement into electricity or vice versa. In other words, they use electromagnetic phenomena to produce electricity or convert it into mechanical energy.
ELECTROMAGNETIC GENERATORS
Electromagnetic generators transform mechanical energy into electriciy. There are two types of generators, depending on the type of current that is produce. Generators that produce direct current are called dynamos, and those that produce alternating current are called alternators
-Dynamos
A dynamo consist of a magnet and a rotary coil. The coil is located between the two poles of the magnet. The ends of the coil have tow semi-circulaar conductors, which form the commutator. These conductors are attached to carbon brushes, which in turn are conected to electrical wires. When electricty is applied to the coil, it rotaters and begins to generate direct current in the coil.
-Alternators
A simple alternator is almost identical to a dynamo, except for the commutator, which consist of two metallic rings connected to carbon brushes, Instead of direct current, this produce altenating current
ELECTRIC MOTORS
An electric motor is device that can transform electrical energy into movement. It uses the forces of attraction and repulsion between a magnet and an elctrically-charged wire.
RELAY
A relay os an elctromagnetic component that works as a switch. When electricity passes through the coil, it acts like a magnet. The coil attracts a moveable metal contact towards another fixed contact.
lunes, 3 de abril de 2017
EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
The movement of electrons though conductibe materials produces effects that hava applications. For example, a hair dryer uses the energy of electrons to produce heat and movement-
HEAT
The energy that an electric current produces as heat is called the Joule Effect. It is expressed by the following formula
E= I2xRxt
Most of the energy that is consumed by radiators and heaters is converted into heat.
LIGHT
-Incandescent bulbs
When an electrc current passes through the meatallic filament of a light bulb, iat produce light. This phenomenon is called incandescence.
-Fluorescent tubes
Inside a fluorescent tube, there is a metallic filament, normally made of tungsten. There is also an inert gas, such as argon, and a small amount of mercury
-Light emitting diodes (LED)
A light-emitting diode (LED) has laters of semiconductor materials. The n-type layer has extra electrons with negatively charged particles.
HEAT
The energy that an electric current produces as heat is called the Joule Effect. It is expressed by the following formula
E= I2xRxt
Most of the energy that is consumed by radiators and heaters is converted into heat.
LIGHT
-Incandescent bulbs
When an electrc current passes through the meatallic filament of a light bulb, iat produce light. This phenomenon is called incandescence.
-Fluorescent tubes
Inside a fluorescent tube, there is a metallic filament, normally made of tungsten. There is also an inert gas, such as argon, and a small amount of mercury
-Light emitting diodes (LED)
A light-emitting diode (LED) has laters of semiconductor materials. The n-type layer has extra electrons with negatively charged particles.
TYPES OF CURRENT
Some electrical devices use batteries and some must ve connected to the electric mains
DIRECT CURRENT
Between the terminals of abattery, there is a continuous, stable flow of energy. of we use a voltmeter to measure the current in a car battery, the result will always be 12 volts. This is called direct current.
In the same way, if we connect a light bulb to a battery, the electrons always flow in the same direction with the same current.
DIRECT CURRENT
Between the terminals of abattery, there is a continuous, stable flow of energy. of we use a voltmeter to measure the current in a car battery, the result will always be 12 volts. This is called direct current.
In the same way, if we connect a light bulb to a battery, the electrons always flow in the same direction with the same current.
ALTERNATING CURRENT
If we measured the voltage of an electrical socket, the results could be represented in a graph like one below;
-The current egins at 0 V and increases to 325V
-The current decreases from 325V to 0V
-The current becomes negative and decreases to -325V
-The current increases to 0V
The variation of any electrical parameter over a period of time is an electric signal.
The tension of voltage of domestic elctricity is an alternating signal beacause it altenates between positive and negative values. Its waveforms is also sinusoidal, with a smiith, regular shape.
THE EFFICIENCY OF ALTERNATING CURRENT
The average power of alternating current is equal to the direct current that is needed to produce the same effect. In te case of an alternating sinusoidal current, the average power would be as follows
Vef= Vmax/√2
TRANSFORMERS
Alternating current can be increased or decreased by a transformer. They consist of two windings made of copper wire. If we apply an alternating current to one of them (V1) it'll produce a certain voltage in the other (V2). The value will depend on the number of times that the copper wire has been wrapped around each winding, represented as n1 and n2:
V1/V2=n1/n2
lunes, 27 de marzo de 2017
TYPES OF CIRCUITS
SERIES CIRCUIT
Two or more elements form a series circuit when the output of one element provide the input for the next elemenat.
In the following diagram, the same current flows through all the elemnts, and the total volatge is the sum of the tensions at the end of each element
1/R=1/R1+1/R2+1/R3+...
Two or more elements form a series circuit when the output of one element provide the input for the next elemenat.
In the following diagram, the same current flows through all the elemnts, and the total volatge is the sum of the tensions at the end of each element
To calculate the total resistance of a circuit, we add the resistance values of each load:
R=R1+R2+R3+...
One example of this type of conection would be a series of generators. The total resistance would be the sum of all the resistance values.
V= V1+V2+V3+...
PARALLEL CIRCUIT
In a parallel circuit, the various components share the same input and output. In other words, the wires from both sides are joined together.
If indetical batteries are connected in paralle, the voltage of the circuit will not increase. However, the total consumption of energy will be shared between the batteries, so each one will last longer.
COMBINATION CIRCUIT
A combination circuit has some elements connected in series and other elements connected in parallel.
In thisa type of circuit, the current remains constant between elements that are connected in series.
At the same time, the voltage remains constant between elements that are connected in parallel
ELECTRICAL QUANTITIES
VOLTAGE OR POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE
In the circuit on the rigth, electrons flow from an electrochemical cell, though a light bulb and the back to the cell.
The amount of energy that a generator can transfer to electrons depends on its voltage (V) or electric tension. This is measured in volts (V)
ELECTRICAL RESISTANCE: OHM´S LAW
The resistance (R) of a material is equal to the voltage divided by the intensity of the electic current wich travels trough the material. This ratio, wich is called Ohm's Law, can be expressed as follows:
Ohm's Law has two forms:
V=RxI and I=V/R
ELECTRICAL ENERGY AND POWER
Electrical energy
If an electric current (I) flows at a particular tension (V) for a certain amount of time (t) we can calculate the energy (E) that is consumed: E=V x I x t
In the circuit on the rigth, electrons flow from an electrochemical cell, though a light bulb and the back to the cell.
The amount of energy that a generator can transfer to electrons depends on its voltage (V) or electric tension. This is measured in volts (V)
If we want to measure volatage, we can use a voltmeter. This device has two wire that must be connected in parallel to the element athat we are checking.
MEASURING ELECTRIC CURRENT
Electric current (I) is the charge or nmber of electrons that flow throuht the cross-section oof a conductor every second. We can express this mathematically as follows:
Electric current is measured in amperes or amps (A) in the International System or SI
ELECTRICAL RESISTANCE: OHM´S LAW
In order to measure the resistance of a lamp, the following experiment was performed with three different circuits
The resistance (R) of a material is equal to the voltage divided by the intensity of the electic current wich travels trough the material. This ratio, wich is called Ohm's Law, can be expressed as follows:
R=V/I
V=RxI and I=V/R
The ohm (Ω) is the unit of electric resistance. The following equation can be used
1Ω=1V/1A
Electrical energy
If an electric current (I) flows at a particular tension (V) for a certain amount of time (t) we can calculate the energy (E) that is consumed: E=V x I x t
In this SI, this electrical energy is measured joules (J)
Electric power
The electric power of a load is the amount of energy that it can transform over a certain amount of time.Electric power is measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW)
domingo, 26 de marzo de 2017
Electric circuit and electronics
AN ELECTRIC CIRCUIT
An Electric circuit is a pathway for the flow of electrons.
Electric current is a continuous flow of electrons through a circuit
PARTS OF AN ELECTRIC CIRCUIT
Electric circuit consist of various parts:
-Generator: Cells and batteries Loads: Light bulbs, Motirs, Resistors, Bells

Switching device: Switches, push buttons, 3-way switches

DIAGRAMS AND SYMBOLS

An Electric circuit is a pathway for the flow of electrons.
Electric current is a continuous flow of electrons through a circuit
PARTS OF AN ELECTRIC CIRCUIT
Electric circuit consist of various parts:
-Generator: Cells and batteries Loads: Light bulbs, Motirs, Resistors, Bells
Switching device: Switches, push buttons, 3-way switches
DIAGRAMS AND SYMBOLS

jueves, 16 de marzo de 2017
Environmental impact
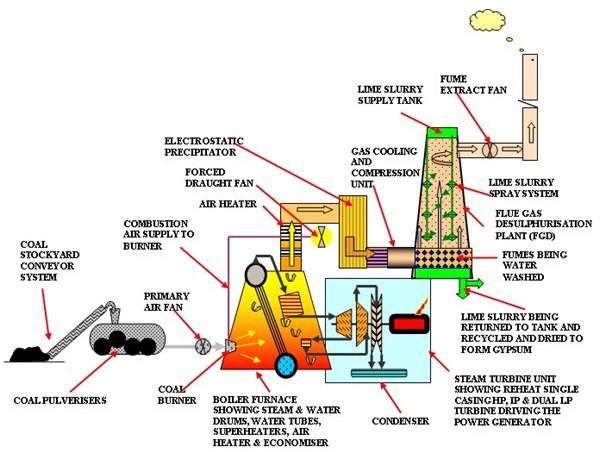
Power stations use products that affect the environment, or example hey require the construction of new buildings and other infrastructure.
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT.
Any proposed new technological project include an environmental impact assessment that are all of the ecological changes that the project could cause in the local área and there also be in the economical and social repercussions of the project.
⤇Wind: It use renewable energy. It has visual and acoustic impacts and the output is low ,strong winds can cause accidents. However, wind farms are clean and help to replace our dependency on fossil fuels.

⤇Hydroelectric: It use renewable energy. It changes the flow of rivers and floods large áreas.
Hydroelectric power stations could generate disasters and dangers to plants and animals. Their output is efficient and high.

⤇Solar: It use renewable energy. These power stations take up a lot of land and installations are expensive. There are risks of burns and blindness, and their output is low. However it's clean and helps to replace our dependency on fossil fuels.

⤇Marine: It use renewable energy. The construcction of these power stations are expensive and affects the environment and the output is low. They are clean and help to replace our dependancy on fossil fuels.
⤇Biomass: It use renewable energy. Their technology is beneficial when it is used properly but it requires an excessive of natural resources. They replace our dependancy on fossil fuels and waste products that go to landfill sites.

⤇Fossil fuels: It use non-renewable energy. These power stations affects the air and the wáter and damage the environment. The pollution of the air causes respiratory ilnesses. Their output is high and efficient.
⤇Nuclear: It use non-renewable energy. They produce radioactive waste and accidents. The waste products are not reciclable. Their output is high and efficient.
Power stations that use renewable energy sources
There are some power stations that use renewable energy for reduce our dependance of fossil fuels that cause many problems in our environment. These power stations generate less energy than the others but they have many advantages:
○They produce less pollution than convetional power stations.
○They have unlimited resources.
○We dont need import so much fuels.
○They are very cheap.
WIND FARMS.
These power stations use the kinetic energy of the wind to produce energy. Wind farms work with a tower, and in the tower a turbine turns when the wind blows.
They must be installed in locations where the wind is strong. The efficiency depends on two factors:
∎The location of the power stations.
∎The number of turbines that are installed.


Wind farms are very cheap in comparaison with other power stations, and they are a totally clean source of energy. The total output of a wind farm depends on the number and size of the turbines.
HYDROELECTRIC POWER STATIONS.
These power stations use the energy of falling wáter to produce energy. Hydroelectric stations work with a recevoir, that acumulates wáter behind a high dam. The kinetic energy produced moves the blades of turbines, and the generator connected in the turbines produce energy. There are two types of hydroelectric power stations:
➝ Conventional hydroelectric power stations: The wáter flows from the recevoir trough a conduit where the wáter is in high pression. Then it flows out into a river.


➝ Pumped-storage hydroelectic stations: The wáter flows to a second recevoir. Then is pumped back to a higher recevoir. These stations are installed where there isnt enough rain to keep the upper recevoir full.

SOLAR POWER STATIONS.
These power stations use energy from rails of sun to generate energy. There are two types of solar power stations:
➦ Solar termal stations; They can use sunlight in two ways:

□ They can absorb sunlight in order to produce heat with solar collectors
□ They can reflect and concéntrate sunlight in one place with heliostats.
In both ways the water is heated to produce steam, that turns the rotor of a generator , which produces electricity.

BIOMASS POWER STATIONS.
Biomass is any organic thing that is produced by natural processes.
There are many types o biomass that we can use to produce energy, but in a biomass power station we use fuel produced by biomass. The steam produced from burn the biomass moves a turbine that is connected to a generator.
 Some adavantages of these power stations are that they use waste materials that would normally end up in landfill sites and they produce less pollution than conventionl thermal power stations.
Some adavantages of these power stations are that they use waste materials that would normally end up in landfill sites and they produce less pollution than conventionl thermal power stations.MARINE POWER STATIONS.
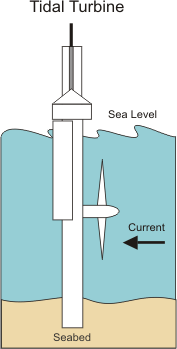
These power stations use the movement of ocean water to produce electricity. However ,they are very expensive and not very efficient. There are various types:
∎ Tidal power stations, that use the energy of tides.
∎ Wave power stations, which use the energy of waves.
∎ Ocean termal conversión stations, that use the difference in temperature between the ocean's surface and deeper áreas to produce energy.

GEOTHERMAL POWER STATIONS.
These power stations use natural heat from the Earth's surface as hot water, steam and hot gases. They can be use in two ways:
It can be used directly to provide hot water for heating and industrial uses.
It can be used indirectly to drive generators and produce electricity.

Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)

































