Power stations that use renewable energy sources
There are some power stations that use renewable energy for reduce our dependance of fossil fuels that cause many problems in our environment. These power stations generate less energy than the others but they have many advantages:
○They produce less pollution than convetional power stations.
○They have unlimited resources.
○We dont need import so much fuels.
○They are very cheap.
WIND FARMS.
These power stations use the kinetic energy of the wind to produce energy. Wind farms work with a tower, and in the tower a turbine turns when the wind blows.
They must be installed in locations where the wind is strong. The efficiency depends on two factors:
∎The location of the power stations.
∎The number of turbines that are installed.


Wind farms are very cheap in comparaison with other power stations, and they are a totally clean source of energy. The total output of a wind farm depends on the number and size of the turbines.
HYDROELECTRIC POWER STATIONS.
These power stations use the energy of falling wáter to produce energy. Hydroelectric stations work with a recevoir, that acumulates wáter behind a high dam. The kinetic energy produced moves the blades of turbines, and the generator connected in the turbines produce energy. There are two types of hydroelectric power stations:
➝ Conventional hydroelectric power stations: The wáter flows from the recevoir trough a conduit where the wáter is in high pression. Then it flows out into a river.


➝ Pumped-storage hydroelectic stations: The wáter flows to a second recevoir. Then is pumped back to a higher recevoir. These stations are installed where there isnt enough rain to keep the upper recevoir full.

SOLAR POWER STATIONS.
These power stations use energy from rails of sun to generate energy. There are two types of solar power stations:
➦ Solar termal stations; They can use sunlight in two ways:

□ They can absorb sunlight in order to produce heat with solar collectors
□ They can reflect and concéntrate sunlight in one place with heliostats.
In both ways the water is heated to produce steam, that turns the rotor of a generator , which produces electricity.

➦ Photovoltaic stations; They work with panels ,that contains many photovoltaic cells, and covert sunlight directly into electricity. Small power installations are use for homes and rural áreas, and they are often istalled in the roof. Excess power is stored in batteries or accumulators.

BIOMASS POWER STATIONS.
Biomass is any organic thing that is produced by natural processes.
There are many types o biomass that we can use to produce energy, but in a biomass power station we use fuel produced by biomass. The steam produced from burn the biomass moves a turbine that is connected to a generator.
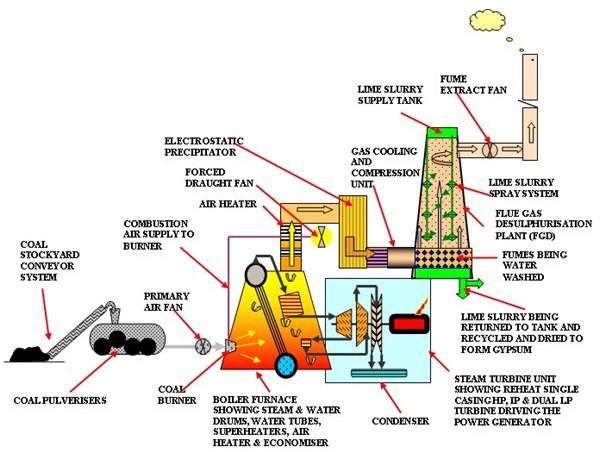
Some adavantages of these power stations are that they use waste materials that would normally end up in landfill sites and they produce less pollution than conventionl thermal power stations.
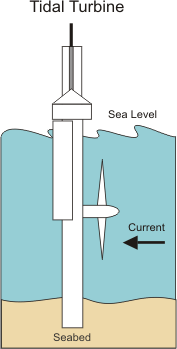
MARINE POWER STATIONS.
These power stations use the movement of ocean water to produce electricity. However ,they are very expensive and not very efficient. There are various types:
∎ Tidal power stations, that use the energy of tides.
∎ Wave power stations, which use the energy of waves.
∎ Ocean termal conversión stations, that use the difference in temperature between the ocean's surface and deeper áreas to produce energy.

GEOTHERMAL POWER STATIONS.
These power stations use natural heat from the Earth's surface as hot water, steam and hot gases. They can be use in two ways:
It can be used directly to provide hot water for heating and industrial uses.
It can be used indirectly to drive generators and produce electricity.

























 Some adavantages of these power stations are that they use waste materials that would normally end up in landfill sites and they produce less pollution than conventionl thermal power stations.
Some adavantages of these power stations are that they use waste materials that would normally end up in landfill sites and they produce less pollution than conventionl thermal power stations.